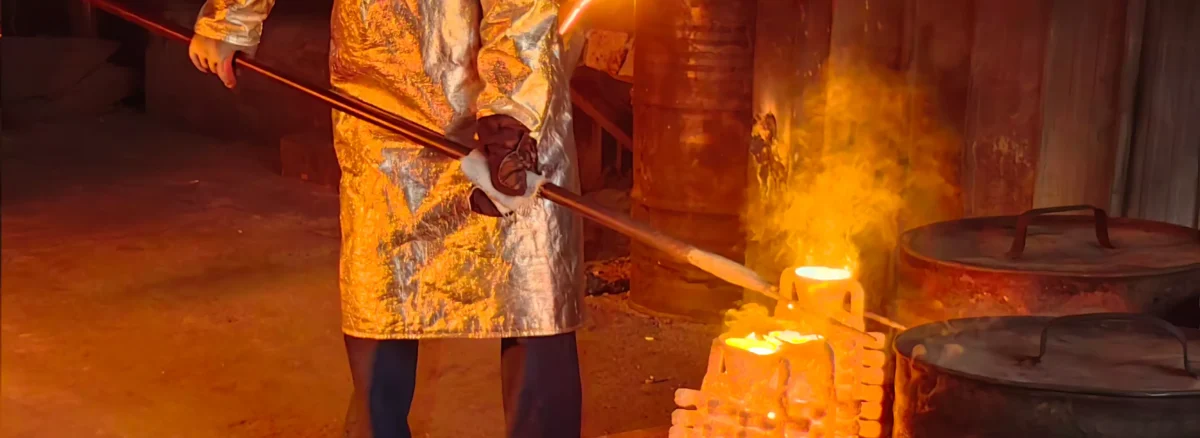
If you are researching and learning about metal casting, or happen to have a project or product that will use it, then this complete guide on metal casting is exactly what you need at this stage. This article is a comprehensive and detailed introduction to metal casting, it will answer all your questions about casting and I’m sure you’ll get something out of reading it. .
What is metal casting?
Metal casting is essentially pouring molten metal liquid into a pre-prepared mold, the cavity inside this mold is the shape of the part we need, and when the metal cools down, we get a part. This is the basic principle of casting.
Casting has been around for thousands of years, dating back as far as 6,000 years ago in China, when bronzes were made by casting. After thousands of years of development, the modern casting process has become very mature and many branches have emerged.
The metal casting process and its segments account for a large proportion of mechanical products, is the main supplier of blanks and parts for the machinery manufacturing industry, the weight of the castings in the internal combustion engine can now account for 70% -90% of the total weight, and can account for 20% of the total weight of the car.
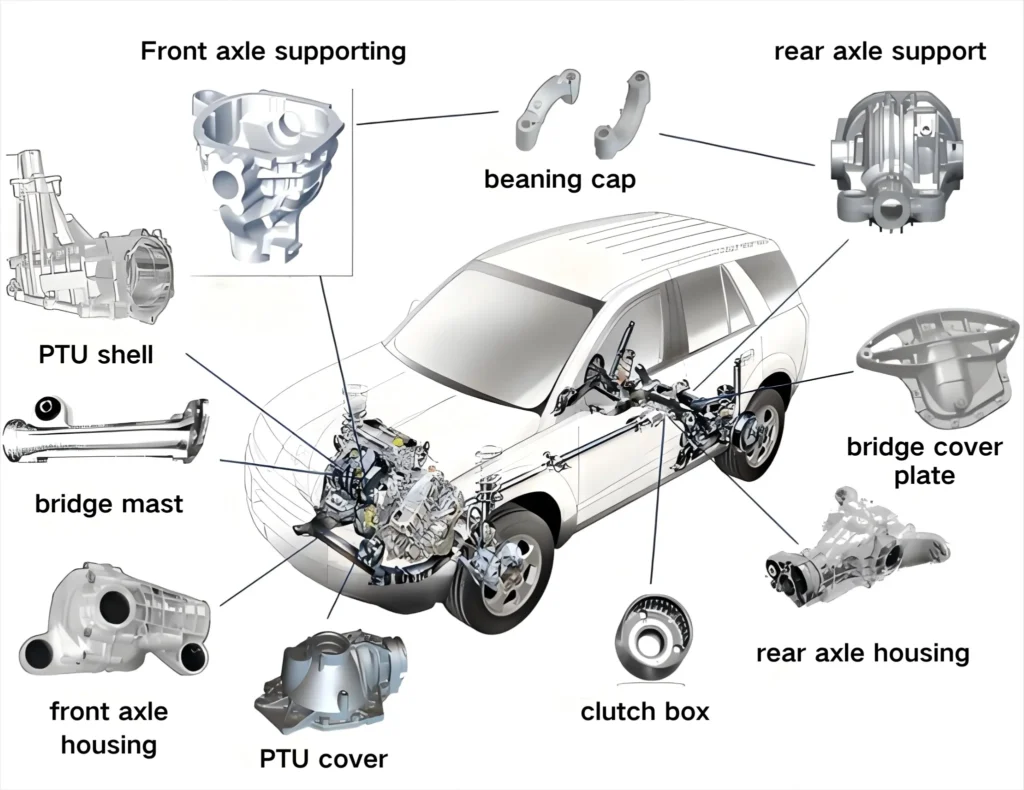
How does metal casting differ from injection molding?
Although metal casting and injection molding are both common molding processes in the manufacturing industry, there are significant differences between the two in terms of materials, product characteristics, and application areas.
metal casting
The main materials used are various metal materials such as iron, aluminum and copper. They are allowed to melt at high temperatures and then poured into molds for cooling. The products that come out in this way are strong and hard, resistant to high temperatures, and have a long product life cycle. But the surface is rough and the dimensional accuracy is low.
Mainly used for engine block, valve body, shell and other mechanical parts.
injection molding
The main material used is plastic, which is allowed to soften at a high temperature and then injected into the mold for cooling and molding by applying pressure to it. Injection molding has high productivity, good surface finish and dimensional accuracy. However, the strength and hardness are low, and it is not resistant to high temperatures.
It is mainly used for plastic parts with high requirements on size and surface, such as electronic product shells, toys, daily necessities and so on.
Why is metal casting important in manufacturing?
In the modern manufacturing industry, many parts with complex shapes cannot be done by ordinary machining centers, five-axis machining centers can do it, but its cost is very high. This highlights the importance of metal casting, which can make a lot of complex parts, and its no problem from a few grams to a few tons or even tens of tons.
There is also its batch production capability, which allows for the rapid production of large quantities of the same product, and also saves the organization money. It is possible to cast a number of zeros that would otherwise need to be interconnected into a single unit, which reduces the need for a large number of welds and connections.
What is the process of metal casting?
The next step will take you through a detailed look at how metal casting goes from raw material to finished product, step by step.
Create the pattern
First you need to have a drawing of the product, of course, if not we can design it for you. Then make a 3D modeling according to the drawing, and next you can manufacture the model.
The main use of this model is to determine the dimensions of the mold cavities, which directly determine the quality of the final product. The model is usually made of wood, wax, plaster or plastic.
Make the mold
Now it’s time to make the molds, which can be divided into disposable models (made of sand, plaster or ceramic) and permanent molds (made of metal) depending on the casting process.
As an example, if you are using precision casting, then your model is made of wax, and then the surface of the model is repeatedly coated with mortar, wait for it to dry, and then heat the mold as a whole to melt and pour out the wax model inside, which creates a cavity, so a mold is ready.

Choose the metallic alloy
This step is where you need to choose what metal material to use, and it depends on your needs, for example, if you want your parts to be lightweight and strong, you can use aluminum alloy as the material. If you want a product with no special requirements, then you can try using gray iron, which is less expensive while its performance is still good.
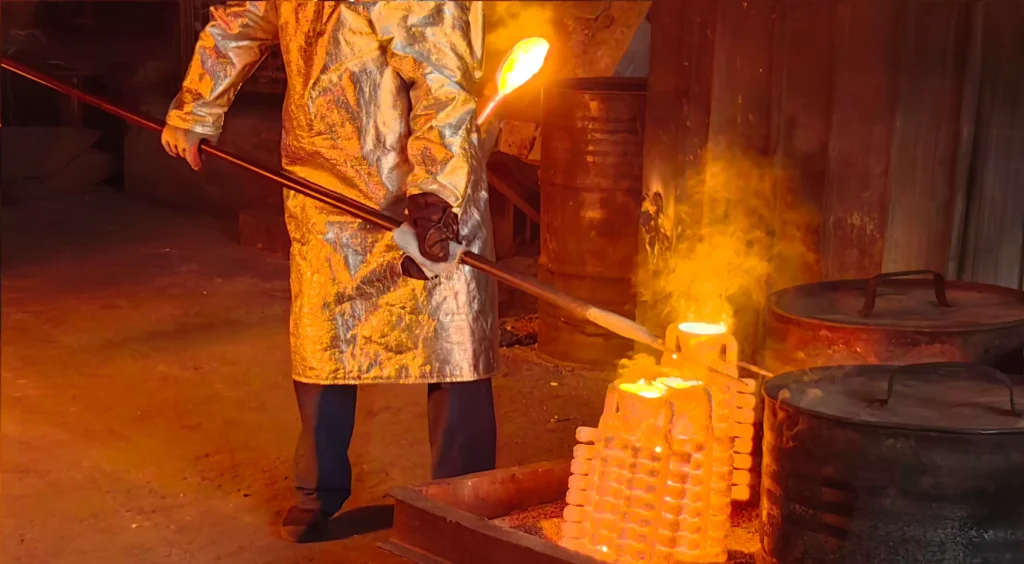
Melt the alloy
The next step is to melt the metal materials of your choice by placing them in a crucible and heating them until they melt. Here are some common melting points of materials used in casting for reference.
| Material Type | Melting Point Range (°C) | Common Applications |
| Gray Cast Iron | 1150-1300 | Mechanical parts, pipes, valves, etc. |
| Ductile Iron | 1150-1300 | High-strength parts, automotive components, etc. |
| Malleable Iron | 1150-1300 | Wear-resistant parts, agricultural machinery parts, etc. |
| Steel | 1300-1500 | Structural components, tools, molds, etc. |
| Aluminum Alloy | 600-700 | Automotive components, aerospace components, etc. |
| Copper Alloy | 900-1100 | Electrical components, decorative items, etc. |
| Zinc Alloy | 390-420 | Die castings, hardware accessories, etc. |
| Magnesium Alloy | 650-700 | Aerospace components, electronic product housings, etc. |
Pour into the mold
When the metal is completely melted into liquid, you can pour it into the mold. If it is a relatively small part, then you can pour it directly into the mold by yourself, if it is a larger part, it will take a team effort and some heavy equipment to complete it. And you can’t go too fast when pouring.
You need to be careful when pouring and make sure to follow the safety guidelines. Make sure to wear protective clothing, gloves and goggles. Maintain a well ventilated environment. Strictly follow the rules and procedures.

Remove the casting from the mold
Once the metal has cooled, you can remove the product, although the cooling process can be lengthy. If you are using a disposable mold, then you will need to break it and remove the product from it. If it is a reusable mold, you will need to remove the product based on its characteristics.
Finishing
This way, your part is complete, but you still need to work on it, such as the extra part of the sprue section, and some extra burrs on the side lengths, to clean it up. This way you get a clean and complete product.
This is the basic process of metal fabrication, of course this is only a generalized process, because there are many different types of casting processes under metal casting, some of which may not be the same.
How long does the metal casting process take?
The length of the casting process affects the supplier’s delivery time, but the duration of the casting process can be affected by many factors, such as the size of the product, the complexity, the material, etc., so the difference can be very large.
- Preparation stage: Including the development of plans, model making and mold making, etc. It will take a longer time, maybe a few weeks or even a month.
- Melting stage: the raw metal is heated to a molten state, which depends on the melting point of the metal and the power of the heating equipment, and generally takes from a few minutes to a few hours.
- Casting stage: this stage is relatively fast, usually a few tens of seconds, if the parts are large, a few minutes will be done.
- Cooling phase: this phase is also more time-consuming, small pieces may be completed in a few hours, large pieces may require more than 10 hours or even a few days, which also has to do with the season, winter cooling will be a little faster, and the opposite is true in summer.
- Post-processing stage: This stage is based on your requirements for the part, including burr cleaning, sprue removal, machining, heat treatment and surface treatment. The time required is uncertain, depending on the number of post-processing procedures, heat treatment and surface treatment will take longer.
Of course this is only an approximate time, if you want to know the exact casting time, you need to take into account the factors mentioned above and combine them with realistic conditions of metal casting process and equipment to make an estimate.
What materials are commonly used for metal casting?
Many metal materials can be used for casting, and they all have different properties, as well as different areas of application.
Magnesium Alloy
Magnesium alloy is the more common metal used for casting, it has a low density and high strength, so it has a high specific strength (the ratio of tensile strength to density), so you can use magnesium alloy if you have a need to reduce the weight of your product. It is suitable for use in components such as automotive parts and aerospace.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum is a versatile casting material that is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, thermally conductive and easy to work with. Aluminum alloys are used in a wide range of applications, such as automotive, aerospace, outdoor products, and electronics.
Iron
Iron can be said to be our usual most common casting materials, mainly divided into gray cast iron and ductile iron. The cost of gray cast iron is relatively low, its casting performance is good, there is a good vibration damping performance, but the strength, toughness is low, is more suitable for the strength requirements are not high, but the vibration damping requirements of high parts, such as boxes, bases and so on.
The strength and toughness of ductile iron is then higher, its strength is close to medium carbon steel. And wear resistance is also very good, the overall performance is better than gray cast iron, but the cost is higher. It is more suitable for parts with high strength and toughness, such as crankshafts, connecting rods, automobile parts and agricultural machinery parts.
Zinc Alloy
Zinc alloy has low melting point, good fluidity and other characteristics, it is most suitable for die casting. The zinc alloy products through die-casting, the size is accurate, the shape can be very complex, the surface is more smooth and other advantages. However, compared with cast iron and cast steel, its strength is low, high temperature resistance is poor. Therefore, it is suitable for the production of electronic components, computer shells, camera parts and so on.
Steel
Steel belongs to the casting material in the most durable, it can be divided into two categories: carbon steel and alloy steel. Carbon steel is divided into low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel with different carbon content, which mainly affects its hardness. The most common alloy steel is stainless steel, which is made of chromium, nickel and some other metals.
Copper Alloys
The use of copper alloy casting is currently more popular a material, it has excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and other properties, often used to manufacture electronic products conductive parts, such as brushes, switches and so on.
| Material | Strength | Ductility | Density | Thermal Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Cost |
| Cast Iron | Medium | Medium | High | Low | Medium | Low |
| Cast Steel | High | High | High | Medium | Medium | Medium-High |
| Cast Aluminum Alloy | Medium | Medium | Low | High | Good | Medium |
| Cast Copper Alloy | Medium | Medium | High | High | Good | Medium-High |
| Cast Magnesium Alloy | High | Medium | Low | Medium | Medium | High |
| Cast Zinc Alloy | Medium | Medium | Low | Medium | Medium | Low |
What are the different types of metal casting?
Metal casting can be divided into many different types of casting below, they are evolved over a long period of time, they have their own characteristics and advantages, take a look together.
Sand casting
Sand casting is one of the oldest casting processes, it has a long history and is still one of the most common types of casting we use. The molds for sand casting are mainly made of high temperature resistant sand, to which a binder is added to increase the hardness of the mold. Commonly used sand types are siliceous sand, water glass sand, oil sand, etc. However, the sand type is determined by the material and size of the casting.
Sand casting can be said to be a very mature casting process, its process is simple, adaptable, and low cost, so it is widely used. But through the sand casting casting out of the parts, dimensional accuracy is not high, the surface is more rough, usually need to be followed by processing.
Sand casting is generally used to manufacture automobile cylinder block, cylinder head, crankcase, agricultural machinery, plowshare, seeding machine parts, harvester parts and so on.
Die casting
Die casting is the process of injecting a molten metal liquid into a metal mold by applying high pressure to it, a process similar to injection molding. Die casting molds are made of high strength and alloys that can be used over and over again.
Die casting has a high fluidity and filling of materials, so die castings are usually made of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, tin and other metals and their alloys.
Die casting of dimensional accuracy and surface finish is high; in the process of die casting, high pressure can make the casting of the internal more tightly less likely to appear air holes; for casting some complex shape, wall thickness of the thinner parts have more advantages. And its high production efficiency, suitable for mass production.
Die casting is suitable for the production of some precision parts, such as blades for airplanes, engine parts, automobile gearboxes and so on.

Precision Casting
Precision casting is to use a wax injection machine to inject wax into the mold to form a wax mold in the shape of the part, and then the wax mold is repeatedly dipped into the mud (usually a mixture of ceramic powder and binder) and mud ash, and when it has a certain thickness, it will be dried, and then it will be put into the dewaxing axe to melt the wax mold to form a cavity, and therefore it can also be called Investment Casting and Lost Wax Casting.
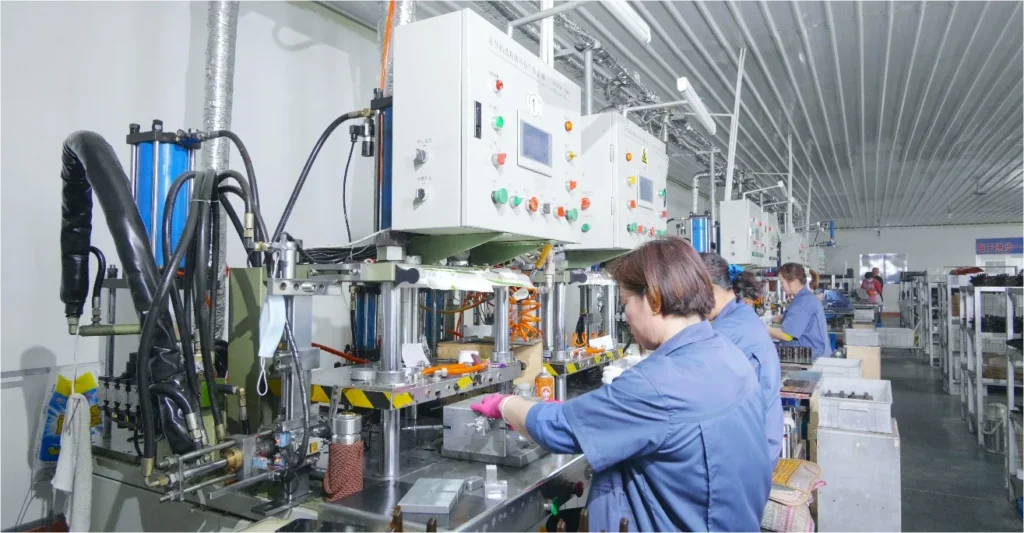

There are two molds for precision casting, one is the mold used for wax injection machine, which can be reused; the other is the mold used for casting after dewaxing, and this is disposable.
The parts that come out of precision casting have high dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface that requires almost no machining at any step other than the sprue. And there are many applications for it, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical.
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting actually involves pouring molten metal into a mold and rotating it at high speeds so that the metal can spread evenly along the inside walls of the mold until it cools. It is possible to cast thin-walled cylinders that cannot be achieved by other methods.
The parts produced by centrifugal casting have high strength and few defects. It can be used to cast pipes, water pipes, gasoline pipes, etc.
gravitational casting
Gravity casting refers to a casting method in which a metallic liquid is allowed to flow freely through the gravitational pull of the earth, filling a cavity or mold to form the initial shape of the casting. The process of gravity casting is simple and easy to operate with high dimensional accuracy of the parts.
Gravity casting is suitable for parts with thicker walls, such as engine blocks, crankcases, turbine housings and blades.
Vanishing Mold Casting (TCM)
Vanishing mold casting is somewhat similar to investment casting, except that it uses foam instead of wax, it takes advantage of the low melting point of the foam, you can use molten metal to make the foam directly gasification, do not need to detach the foam from the mold, and pour the metal directly into the mold, you can also be understood as a simplified version of investment casting.
The advantages of disappearing mold casting you can refer to the precision casting, the cost will be slightly higher than the precision casting, because the foam is disposable, used up and gone.
What are the industrial applications of metal casting?
Since metal casting is a molding process, almost every industry uses casting to make parts to a greater or lesser extent, so that casting is highly customizable, and here are some of the applications of casting in some industries.
- Automotive industry: Cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, intake tubes, crankcases and other accessories for automotive engines.
- Aerospace: turbine shells, blades, brackets, etc. for space engines.
- Railroad industry: wheels for trains, brakes, connections, buffer housings, etc.
- Marine industry: propellers, rudders, anchors, etc. for ships.
- Machinery industry: machine tool beds, cases, etc.
- Agricultural machinery: accessories for agricultural machinery, plowshares, tine harrows, connectors, etc.
- Construction machinery: such as engine mounts, booms, buckets, etc.
- Construction: Valves, pipes, etc. for construction.
How durable are cast metal products?
The durability of a cast product depends mainly on its material, heat treatment and use. Different materials have different hardness, strength and corrosion resistance, for example, cast steel is more durable than cast aluminum. And castings that are heat-treated perform better and last longer than those that are not. Their service life ranges from a few months to decades.
When the casting is completely unusable, it can be recycled, collected back and molded into new parts.
Is there a variation in the thickness of cast metal products?
The thickness will vary, depending on the design requirements of the drawing and the casting method used. For example, die casting can make parts with very thin wall thickness, and the thickness of each part of the same product can be different, but this is more difficult for sand casting.
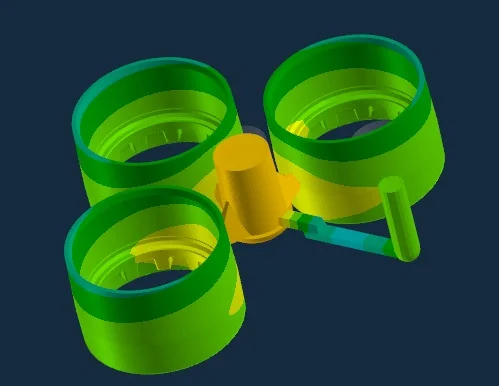
You can also use mold flow analysis to observe them before casting.
What is the future of metal casting?
Casting has a history of more than 6,000 years, can be extended down, which can explain its importance to our development, it is a very convenient method of metal molding, and the cost is also relatively low.
Future casting will use more new materials, such as titanium alloys and some composite materials. And in order to meet the demand for lightweight and high performance, the casting design will become more complex, which also requires casting towards the direction of refinement.
Emerging 3D printing technology has a certain impact on casting, 3D printing is mainly through the method of laser sintering to print metal, it has a high degree of freedom of design, can produce complex shapes and have internal features of the parts, but also reduce the output of scrap mold making, tooling and labor.
However, current 3D printing technology has certain limitations, such as the slow production speed of a single 3D printer, the high cost of producing small batches, the inability to produce large parts, and the limited range of materials to choose from.
Still using metal casting today?
Due to the low cost of casting, customizable, recyclable, and can be mass-produced, it is still widely used in various industries, some newly developed products or parts not available on the market, the choice of casting process is inevitable.
What are the advantages of metal casting?
Here are some of the more obvious advantages of casting, so you can see if this is what you need too.
- It can produce complex parts that cannot be machined by machining and forging, and casting is particularly well suited to making parts with complex shapes in cavities, making it highly customizable.
- Unlike other machining methods that require the size and material of the part, casting has no hard and fast requirements for the size and material of the part, and the weight of the part can be done from a few grams to a few tons or even a few hundred tons.
- For high-volume production, casting is a very cost-effective manufacturing method that allows for a high degree of automation, reduced labor costs, and the use of relatively inexpensive molds.
- Casting can also save you the cost of time, the product is basically a complete set of processes down in the casting, there are few stops in the middle, which can save you more time.
- Casting can also simplify the production steps for your products, for example, precision casting can save you machining steps, you can use directly, or some surface treatment.
What are the disadvantages of metal casting?
Here are some of the disadvantages of casting, which you must know before you use casting to manufacture parts so that you can consciously look to circumvent them.
- The surface finish of some casting methods is not very good, for example, parts made from sand casting will have hanging sand, and then you need to blast them.
- When using casting, the surface or interior of the part may be prone to porosity, which is caused by the fact that the air inside the mold is not completely eliminated during casting, which is a very common problem in casting.
- The same iron parts, casting is not as good as forging performance, this is because in the forging parts will be subjected to a lot of pressure, resulting in the internal organization of the metal is more compact, so the mechanical properties will be better than casting parts.
- For small quantities, casting may not be as effective as other manufacturing methods, both large and small quantities require a mold to be made first, and the cost of that mold may be more than the profit of even a small quantity of product.
Is metal casting expensive?
The cost of casting consists of the following main aspects.
- Material Costs: The materials will mainly be metals used for casting, type sand for molds, adhesives, and so on. It mainly depends on what metal you are going to use, iron is the cheapest, while copper will be very expensive.
- Mold Cost: The cost of the mold is also expensive, including design and manufacturing and maintenance. The cost of the mold can be diluted if it is produced in large quantities.
- Other costs: the rest is some labor, energy costs are not very high. If subsequent processing is required then more processing costs will be incurred.
Choosing the right metal casting process
Here are some of the factors you need to consider when choosing a casting process and how they fit into that process.
Size and shape
If your product shape is complex and relatively large, you can choose sand casting and investment casting, these two processes of mold making is more flexible, suitable for casting complex shape parts.
If your product shape is simple and not very big, but the quantity is more, you can choose die casting or low pressure casting, they are high production efficiency and suitable for mass production.
Precision and surface quality
Die casting and precision casting can produce castings with high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish. If you have lower requirements for casting accuracy and surface, then you can choose sand casting and shell casting.
production volume
Die casting is suitable for high volume production due to its high productivity. If it is medium volume you can try shell casting, which uses molds that can be reused. If it is small batch production you can use sand casting or precision casting, they use molds with relatively low manufacturing costs and are suitable for small batch production.
makings
Cast steel and cast iron are more suitable for processing by sand casting. Aluminum alloys, zinc alloys and magnesium alloys are suitable for die casting because of their lower melting points. Some precious metals and insoluble metals are more suitable for precision casting, which can precisely control the shape and size of castings.
Metal Casting Terminology
Here are some of the more common terms used in the foundry industry that you can learn about to help you know what they’re talking about when you talk to suppliers in the future.
- Pattern: This is a 1:1 replica of the part to be cast and is used to make molds.
- Mould: A cavity made from Pattern and used to pour molten metal into it to form parts.
- Core: A removable part placed inside a mold to form features inside a casting.
- Gating System: The channel through which molten metal is introduced into the mold.
- Riser: A place where molten metal is stored to fill the voids created by the shrinkage of the casting as it cools.
- Draft: The angle between the product and the mold, which facilitates the pulling of the product out of the mold.
- Vent: A number of small holes in the mold that help gas escape during the casting process.
- Shakeout: The process of removing a fully cooled casting from the mold.
- Fettling: The process of removing more than metal from a casting.
What are the common defects in metal casting?
stoma
It is the existence of voids in the casting, these pores will reduce the gradual strength, airtightness and the ability to withstand pressure, serious may be in the use of the process of direct scrapping.
The cause of porosity may be that the molten metal contains too much gas; or the casting speed is too fast, resulting in too little time for the gas to be removed; or the mold has poor venting, resulting in the gas being unable to be removed and being trapped in the casting.
You can try to reduce the gas content in the metal solution, keep it even when pouring, and increase the air permeability of the mold.
Shrinkage and Shrinkage
In the process of casting cooling, the metal will shrink and form cavities inside or on the surface of the casting, shrinkage is a number of small scattered shrinkage holes. Usually distributed in the vicinity of the sprue, the root of the riser or thicker wall thickness. This will significantly reduce the mechanical properties of the casting, and easy to be corroded.
Shrinkage or shrinkage is usually caused by too low temperature during casting, poor riser fill shrinkage, broken flow; or too fast cooling. You can increase the temperature of the mold before casting, or design a pressurizing device at the riser, or you can accurately design the casting system and choose the right casting temperature.
crackles
Cracks are well understood, they are cracks that occur due to excessive stress while the casting is cooling and solidifying. If you use a casting with cracks, it will affect its mechanical properties and will likely break along the crack during use.
Metal mold casting is easy to make the casting cracks, this is because the metal mold is very hard, there is no concession, it is easy to lead to excessive stress inside the casting, resulting in cracks. In addition, opening the mold too early or too late, the coating layer is too thin are prone to cracks.
You can adjust the thickness of the coating and make the cooling rate of each part of the casting as close as possible to avoid too much stress forming inside and causing cracks. Paying attention to the working temperature of the metal mold, adjusting the mold inclination, etc. can effectively avoid cracks.
cold storage
Cold segregation is a type of penetration seam or a surface pinch at the rounded edges, which is separated by the oxidized skin in the middle, and the metal is not fully fused together. This problem affects the mechanical properties and service life of the casting, and is not aesthetically pleasing.
The defect of cold segregation is mainly due to the irrational design of mold scheduling, too low working temperature, bad location of sprue, or too slow speed when casting.
If you encounter this kind of problem, you can try to design the mold in a reasonable arrangement of the location of the sprue and exhaust system, increase the temperature of the mold during casting, or you can also use mechanical vibration casting and other methods to avoid this problem.
slagging
Slagging refers to the presence of impurities or oxides in the casting, which can seriously affect the gradual quality and performance. This is most likely when you use the raw material is not pure, the melting process is not sufficient slag removal, or the casting environment is poor.
You can use high-quality raw materials, try to get rid of impurities in the melting process, and keep the environment tidy when casting, which can effectively avoid the appearance of slagging problems.
trachoma
A sand eye is a hollow inside or on the surface of a casting that is filled with sand, usually a rounded cavity. The causes of this problem may be that the surface strength of the sand core is not high, burnt or not fully cured; the size of the sand core does not match the size of the outer mold, and the sand core is crushed when the mold is closed; or the friction between the ladle and the sprue occurs, and the fallen sand flows into the mold along with the metal liquid.
In order to avoid this situation, in the production of sand must be strictly in accordance with the production process, and to ensure that the size of the appropriate; and then in the casting to avoid the sprue and sprue distance is too close to cause friction.
Myths about metal casting
“Molds don’t need to be preheated.”
Many casting factories think that the mold does not need to be preheated, just pour directly, which can also save time and cost. But they don’t know that if they don’t preheat the mold, when the metal liquid is injected into the mold, it will cool faster, which will increase the risk of defects such as porosity and shrinkage.
This will not only not save time and cost, but will increase the scrap rate, increase the cost and rework time, and even reduce the product qualification rate and affect the customer’s delivery date.
So please do remember! Preheating the mold is an important step in ensuring the quality of your castings.
“A simple design of the casting system will do.”
You may think that the pouring system only needs a simple design and does not need to be very fine, in fact, this is a misunderstanding. If your pouring system is not reasonably designed, it will lead to the metal solution can not flow into the mold in time when you are pouring, which may cause sand washing, slagging, porosity and other problems.
The right pouring system will allow the metal liquid to fill the cavity smoothly and evenly, which will prevent many problems from occurring.
“The casting speed doesn’t have to be controlled.”
There are many front-line workers think that the faster the casting speed the better, so as to improve efficiency, this is a wrong idea. Pouring too fast will cause the situation of rolled gas, affecting the quality of the casting, but also lead to hot liquid splash, increasing the potential safety hazards.
“The quality of cast parts is uncontrollable.”
There are a lot of people who think that once the casting is done, I can’t control the quality of this part because I can’t visually see if there is any problem with the part through the mold, and I can only see the problem when I take it out of the mold, so this quality is not under control.
To address this problem, we can through the raw materials, process parameters, mold design and other aspects of strict control, which can effectively ensure the quality of casting parts.
“No need to design an exhaust system, the gas will be removed from the vent.”
This is a wrong idea, the gas in the mold during casting can’t all be discharged from the risers, the exhaust system is a very important part of the design of the mold.
The absence or poor design of an exhaust system can result in gases not being able to escape smoothly, increasing the risk of porosity and other defects.
Choosing the right metal casting partner
Choosing the right supplier can be difficult, but choosing the right supplier will help you avoid a lot of trouble and your project can be completed smoothly. Here are some suggestions for choosing a casting supplier, I hope it can help you.
Qualifications and Experience
- Qualification: First of all, you have to see if the supplier has any relevant quality certificates, such as IOS9001, IAFT16949, etc. These can let you know whether they have a perfect product quality management system.
- Industry experience: You need to find out if the supplier has a lot of experience in your industry or your type of product, and if you can, it’s a good idea to provide some success stories.
- Technical ability: whether the supplier has the technical ability of the casting process you need, to see if their technicians are professional.
- Equipment and facilities: In this regard, it is best if you can go to the supplier’s site and make a field trip to see if their equipment and facilities can meet your production needs.
Product Quality and Control
- Quality control: examine whether they have been seriously practicing quality control system, including raw material inspection, process control, finished product inspection, etc..
- Failure Rates: Find out what their product failure rates are and how they are dealing with these failures.
- Means of testing: See if their testing equipment is advanced and complete, such as Coordinate Measuring Machine, Direct-Reading spectrometer, Rockwell Hardness Tester, Metallurgical Microscope and so on.
Capacity and Delivery
- Capacity: Whether the supplier’s production capacity can meet the demand of your order, including production lead time and capacity.
- Delivery: see if they can deliver products on time and their ability to respond to expedited orders.
- Flexible production: the ability to produce flexibly and adapt to changes in order quantities and product types.
Service and Support
- Technical support: whether the supplier can provide technical support, such as helping you design products, optimize processes and materials, etc.,
- After-sales service: whether it can provide perfect after-sales service system, whether it can solve product quality problems in time and how to solve them.
- Communication and cooperation: whether communication with you is proactive and positive, and whether you are willing to work closely with you.
Costs and Prices
- Price: do more price comparisons and find one that is cost effective.
- Cost structure: whether the supplier’s offer is detailed and reasonable, the more detailed the more serious, such as raw materials, labor, outsourcing and so on.
- Payment Methods: Understand the payment methods and terms of business and choose the one that suits you best.
You can make reference to the above information, of course, there are also aspects such as location, corporate culture, environmental awareness, etc. that can be examined.
Reach a Verdict
I hope this article is helpful to you, can let you have a detailed and systematic understanding of metal casting, if there is something wrong please help us point out, we will accept it with an open mind.
If you need services in casting, you can also contact us, we have rich experience and professional technical team.





